Themes > Current Issues
01.09.2009
Who Needs these Taxes?
C.P. Chandrasekhar
It is
not just a revamp, claims the government, but altogether new. After
many rounds of reduction of the marginal tax rate and years of tinkering
with the structure of direct taxes it claims to have decided to drastically
alter the direct tax regime. To that end it has launched a debate
that would lead up to the introduction of legislation to put in place
a new direct tax code. The discussion paper accompanying the draft
code attempts to draw attention to a number of features of the new
code: the definition of income, clarity regarding who can be taxed
and the treatment of exemptions. But discussion on the code is likely
to be dominated by the extent of taxation of personal and corporate
incomes that the new regime would involve.
In this regard there is one aspect of the new code that is welcome.
It seeks to rationalize the innumerable tax exemptions given to both
high-income personal income tax payers and corporations. The consequence
of this would be enhanced revenue generation and a greater degree
of transparency in the tax structure. It would also possibly lead
to greater equity, since most tax exemptions are either directed at
or more easily exploited by those in higher income tax brackets.
Budget documents for 2009-10 estimate that the “tax expenditures”
on account of foregone taxes during 2008-09 amounted to Rs. 68,914
crore in the case of corporate taxes, Rs. 5116 crore in the case of
non-corporate (partnerships, associations of persons, bodies of individuals)
tax payers and Rs. 34,437 crore in the case of income taxes. This
amounts to around 17 per cent of the gross tax revenues which accrued
to the central government according to the revised estimates for that
year. Recouping a significant share of this would make a considerable
difference to the budgetary position of the government and increase
its fiscal manoeuvrability.
However, if this and greater transparency and equity were the objectives
that the government was pursuing then a revamp of the existing tax
law to get rid of a wide range of unnecessary exemptions would have
been adequate. That the government is pursuing objectives other than
these is clear from its unorthodox decision to include in the documents
for discussion on the proposed Direct Tax Bill a proposal for a new
structure of direct tax rates. That structure could lead to a sharp
reduction of taxes currently paid by individuals and corporates in
different tax brackets under the present tax regime.
The way this is to be ensured is a significant widening of the tax
slabs leading to a situation where individuals would pay only 10 per
cent tax as long as they remain in the slab Rs.1,60,000 to Rs. 10,00,000,
20 per cent in the slab Rs.10,00,000 to Rs. 25,00,000 and 30 per cent
thereafter. Further, the corporate tax rate is to be reduced from
30 per cent to 25 per cent and the minimum alternate tax (MAT) is
to be calculated on the value of gross assets, 2 per cent of which
will have to be paid at the minimum by all non-banking companies.
Currently, the income tax payer pays 10 per cent tax on income between
Rs. 1.6 lakh and Rs. 3 lakh, 20 per cent between Rs. 3 lakh and Rs.
5 lakh, and 30 per cent beyond Rs. 5 lakh. This means, for example
that an individual who earns a lakh of rupees every month by way of
taxable salary will see a substantial reduction in the amount of income
tax paid. Moreover, the ceiling on tax-free acquisition of savings
instruments has been increased from Rs.1 lakh to Rs. 3 lakh, even
though the range of instruments eligible for that concession has been
reduced.
By specifying these rates and ranges, even while indicating that they
are also subject to discussion, clearly ties the hand of the government.
Taxes, which are increasingly seen as “hurting” the tax payer and
not as financing beneficial public provision, are such that once the
government proposes a level it can go downwards from there but not
upwards without opposition. This implies that the government has chosen
to significantly cut rates by widening tax slabs and adjusting the
number of rates.
The government’s own view is that such comparisons between the proposed
direct tax regime and the existing one are not valid, because what
we have is a structural transformation in regime. One way of interpreting
that statement could be that it is implicitly declaring that the potential
reduction in revenues as a result of wider slabs and lower rates would
be more than neutralised by the reduction in exemptions under the
proposed regime and by the increased compliance that a lighter tax
regime would encourage. For example salaries in the private sector
are expected to be computed on a cost-to-company basis and the imputed
rental value of rent free accommodation (for example) is to be treated
as part of the salary.
The danger here as can be seen even in the early responses to the
draft code is that the debate in the run up to legislative action
would force the restoration of a range of exemptions while sticking
with the proposed new slabs and rates. Moreover, monitoring whether
value of perquisites are actually computed and included in salary
would be difficult and evasion through such exclusion can be as much
or higher than in the case of evasion of post-exemption income and
tax calculations. The expected quid-pro-quo may not materialise and
revenues may in fact decline.
Given this, the belief that the new code would contribute to an increase
in tax collections is largely based on the faith that reduced tax
rates would contribute to better compliance. Needless to say, this
faith in the “Laffer curve” is neither theoretically nor empirically
grounded. In the event, the new tax code is ill-advised for at least
two reasons. The first is that it comes at a time when despite the
consensus that public capital formation and public expenditure on
social infrastructure and social protection are grossly inadequate
in India, the deficit in the budget of the central government is rising.
Even though there are expectations that the deceleration in growth
in India induced by the global crisis is hitting bottom, there is
substantial agreement that the government must keep expenditure high
if the rate of growth is not to slump further. This would lead to
inflation if it is financed by borrowing rather than by a draft on
private savings through taxation given the fact that food price inflation
is already high and a truant monsoon is likely to intensify supply
constraints. This then is the least propitious time to launch an adventurous
experiment in resource mobilisation involving a cut in direct tax
rates.
But the case against the code is not just short term. It would also
abort the much-needed correction of the decline and stagnation of
the tax-GDP ratio at the centre. One striking feature of the 1990s,
which was the first decade of accelerated economic reform, is that
despite evidence of reasonably good growth rates and signs of growing
inequality, there was no improvement in the Centre’s ability to garner
a larger share of resources to finance expenditures it considered
crucial. Even when corporate profits and managerial salaries were
reported to be rising sharply, taxes did not appear as buoyant. The
Central tax GDP ratios in India were declining for much of this period.
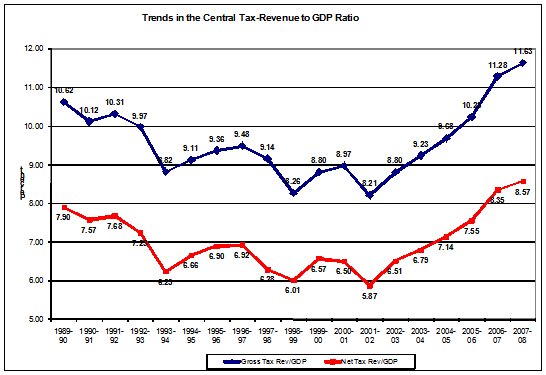
And despite the increase in the ratio in recent years, they exceeded
the level they were at in 1989-90 only in 2006-07 (Chart ). Despite
high growth, improved profitability and signs of increased inequality
(which should improve tax collection), the increase has been adequate
to just about put the tax GDP ratio back to its immediate pre-liberalisation
levels. Thus an effort to raise this ratio even further is what is
called for.
If these imperatives have been ignored in the new code it must be
because of the view that households taxed lightly would increase their
consumption and firms taxed lightly would invest more, and enhance
consumption and investment would drive growth. There are three problems
with this argument. First, it underestimates the role that public
expenditure in general and public capital formation in particular
plays in crowding in private investment, as amply illustrated by past
Indian experience. Second, it privileges GDP growth even at the cost
of reducing the role of direct taxation in moderating the inequalising
character of recent economic growth. Finally, it completely ignores
the important role of tax-financed public expenditure in alleviating
poverty, providing social protection and advancing human development.
The tax code is a signal that UPA II plans to continue with the policy
of cajoling private capital into investing for growth with concessions
that have adverse equity and welfare implications.
© MACROSCAN 2009